Washington, DC, was sizzling and humid on June 23, 1993, however nobody was sweating greater than Daniel Goldin, the administrator of NASA. Standing exterior the Home chamber, he watched nervously as votes registered on the digital tally board. The area station wasn’t going to make it. The US had spent greater than $11 billion on it by then, with hundreds of kilos of paperwork to point out for it—however zero kilos of flight {hardware}. Whether or not there would ever be a station got here down, now, to a cancellation vote on the Home flooring.
Politically, the area station was one thing of a wayward orphan. It was a nine-year-old Reagan administration initiative, expanded by George H.W. Bush because the centerpiece of a would-be return to the moon and an try to achieve Mars. When voters changed Bush with Invoice Clinton, Goldin persuaded the brand new president to maintain the station by pitching it as a post-Soviet reconstruction effort. The Russians had been nice at constructing stations, which might save NASA a fortune in R&D. In flip, NASA’s funding would hold Russian rocket scientists employed—and fewer more likely to freelance for hostile overseas powers. Nonetheless, dissatisfaction with NASA was a bipartisan affair: everybody appeared to agree that the company was bloated and ossified. Consultant Tim Roemer, a Democrat from Indiana, wished to make some massive modifications, and he launched an modification to the NASA authorization invoice to kill the station as soon as and for all.
Goldin had made greater than 100 cellphone calls within the day and a half earlier than the vote, hoping to sway lawmakers to endorse the station, which he noticed as crucial for learning biomedicine, electronics, supplies engineering, and the human physique in a totally alien atmosphere: microgravity. Issues right down to the molecular stage behave profoundly otherwise in area, and flying experiments per week at a time on the shuttle wasn’t sufficient to be taught a lot. Actual analysis required a everlasting presence in area, and that meant an area station.
Supporters of the area station had gone into the vote anticipating to win. Not by a lot—20 votes, perhaps. However the longer the vote went on, the nearer it bought. Both sides started cheering because it pulled forward. The 110 new members of Congress, none of whom had ever earlier than forged a vote involving the station, revealed themselves to be much less dependable than anticipated.
Lastly, the tally reached 215–215, with one vote remaining: Consultant John Lewis of Georgia, a civil rights legend. As Lewis walked down the corridor towards the legislative chamber, Goldin’s legislative aide, Jeff Lawrence, instructed the administrator to say one thing—something—to win him over. As Lewis walked by, Goldin had just one second, perhaps two, and the very best he may get out was a uncooked, trustworthy, “Congressman Lewis, the way forward for the area program is dependent upon you.” He added: “The nation is relying on you. How will you vote?”
Lewis smiled as he walked by. He mentioned, “I ain’t telling you.”
The station, later named the Worldwide Area Station, survived by his single vote, 216–215. 5 years later, Russia launched the primary module from Kazakhstan, and since November 2000, not a single day has elapsed with out a human being in area.
NASA designed the Worldwide Area Station to fly for 20 years. It has lasted six years longer than that, although it’s exhibiting its age, and NASA is presently learning tips on how to safely destroy the area laboratory by round 2030. It will contain a “deorbit automobile” docking with the ISS, which is the scale of a soccer discipline (together with finish zones), and firing thrusters in order that the station, which circles the Earth at 5 miles per second, slams down squarely in the course of the Pacific Ocean, avoiding land, harm, and the lack of human life.
Because the scorched stays of the station sink to the underside of the ocean, nevertheless, the story of America in low Earth orbit (LEO) will proceed. The ISS by no means actually grew to become what some had hoped: a launching level for an increasing human presence within the photo voltaic system. However it did allow elementary analysis on supplies and drugs, and it helped us begin to perceive how area impacts the human physique. To construct on that work, NASA has partnered with non-public corporations to develop new, industrial area stations for analysis, manufacturing, and tourism. If they’re profitable, these corporations will deliver a few new period of area exploration: non-public rockets flying to non-public locations. They may even reveal a brand new mannequin during which NASA builds infrastructure and the non-public sector takes it from there, liberating the company to discover deeper and deeper into area, the place the method might be repeated. They’re already planning on doing it across the moon. In the future, Mars may comply with.
From the daybreak of the area age, area stations had been envisioned as important to leaving Earth.
In 1952, Wernher von Braun, the first architect of the American area program, known as them “as inevitable because the rising of the solar” and mentioned they’d be integral to any sustainable exploration program, mitigating value and complexity. Certainly, he proposed constructing an area station earlier than a moon or Mars program, in order that expeditions would have a logistical manner station for resupply and refueling.
“Going into the 1960s, there’s a whole lot of consensus and momentum round the concept that area goes to be a three-step course of,” says historian David Hitt, coauthor of Homesteading Area: The Skylab Story. The 1st step, he instructed me, is transportation. You’ve bought to depart Earth in some way, which implies creating the infrastructure to construct human-safe rockets and launching them. Step two is habitation. You want a spot to dwell as soon as you might be in area—for its personal sake as a science laboratory, and likewise as a logistical waypoint between Earth and different celestial objects. “Upon getting transportation and habitation,” he says, “you’ll be able to take the next step, which is exploration.”
The mindset modified after the Soviet Union beat the US to orbit, first with its Sputnik I satellite tv for pc in 1957 and once more when cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin grew to become the primary man in area in 1961. President John F. Kennedy dedicated the nation to touchdown a person on the moon and returning him safely to Earth “earlier than this decade is out.” It was an outrageously bold purpose, on condition that NASA had solely managed to launch a human to area three weeks earlier. “It required shifting rapidly, and the way in which you do that’s to take the three-step plan and do away with step two,” Hitt instructed me. “Because it turned out, in the event you skip the habitation stage, it really works—the US bought to the moon, however did so in a manner that didn’t lay the groundwork for the long-term sustainability of this system.”
“Even going again to the Mercury program, the purpose was all the time the moon. Skylab is the primary time that area itself grew to become the vacation spot.”
David Hitt, historian
We’re nonetheless engaged on that. Two years after the ultimate Apollo mission, NASA launched the primary American area station, Skylab. Tailored from the second stage of a Saturn V moon rocket, it was huge: 99 ft (30 meters) lengthy and by far the heaviest spacecraft ever launched. NASA would ultimately launch three missions of three astronauts every to the station, the place they’d carry out greater than 100 experiments.
“In a really possible way, Skylab was the primary American area mission,” Hitt says. “Earlier than Skylab, we had been flying moon missions—even going again to the Mercury program, the purpose was all the time the moon. Skylab is the primary time that area itself grew to become the vacation spot.” Its targets had been foundational to what would later come. “The massive factor that Skylab taught us is that human beings can, in actual fact, dwell and work lengthy durations in an area atmosphere. If we’re critical about going to Mars, you [may] spend manner longer in area than you’re going to spend on the Martian floor.”
Skylab stays the one area station constructed and launched solely by the US. In 1986, the Soviet Union launched the primary module of Mir, a modular area station constructed like Lego blocks, one section at a time. As a result of NASA had discontinued the Saturn V rocket, the company essentially adopted the identical modular station mannequin, ultimately partnering with Russia and different international locations to construct the ISS. In the present day it shares the skies with Tiangong, China’s everlasting area station, the primary module of which launched in 2021. None of those stations have acted as moon or Mars manner stations within the von Braun mildew; to fulfill that requirement, NASA is creating a future station known as Gateway that’s supposed to orbit the moon. Its first module may launch subsequent yr.
Though they by no means grew to become transportation hubs, every area station has superior the crucial reason for studying what lengthy stretches of area do to the human physique. (Russian cosmonaut Valeri Polyakov, who flew on Mir, holds the all-time report for steady spaceflight, with 437 days.) Researchers nonetheless have a relative paucity of data about how the physique responds to area. On Earth, now we have the collective expertise of greater than 100 billion human beings throughout 300,000 years, and nonetheless a lot concerning the human physique stays a thriller. Why will we yawn? What ought to we eat? Fewer than a thousand individuals in 63 years have ever been to area. Such research can solely happen on everlasting area stations.
“In the course of the shuttle program, we had been learning the results of only a shorter-period spaceflight—a pair weeks—on the human physique,” Steven Platts, chief scientist of NASA’s Human Analysis Program, instructed me. Among the many issues was “orthostatic intolerance,” which is the physique’s incapability to control blood stress. It affected a few quarter of crew members who returned from area. As soon as NASA and Russia launched the ISS and spaceflight durations elevated from weeks to months, that quantity leaped to 80%. “We spent a whole lot of time making an attempt to tease out that mechanism. And we ultimately got here up with countermeasures in order that that danger is now thought of closed,” he says.
Different challenges embody spaceflight-related neuro-ocular syndrome, which is a change within the construction and performance of the attention, one thing researchers recognized about 10 years in the past. “We didn’t actually see it with the shuttle, however as we began doing increasingly more station missions, we noticed it,” Platts says. They’ve additionally recognized small, structural modifications within the mind however have but to determine what meaning in the long run: “That’s a comparatively new danger that we didn’t learn about earlier than the area station.”
General, he says, the flexibility of the human physique to control its operate in area is “wonderful.” His group is engaged on about 30 dangers to people posed by area exploration, which it classifies in a color-coding scheme. Inexperienced points are effectively managed. Yellow dangers are of average concern, and crimson ones should be solved earlier than missions are potential. “Proper now, for low Earth orbit there aren’t any crimson. Every part is yellow and inexperienced. We perceive it fairly effectively and we will take care of it. However as we get to lunar, we see extra yellow and a few crimson, and as we get to Mars, we see extra crimson but,” Platts says. “There are issues that we all know proper now are an issue, and we’re working onerous to attempt to determine them out, both from a analysis standpoint or an engineering standpoint.”
Some issues can solely be studied as we enterprise farther into area—the long-term results of Mars mud on the human physique, for instance. Others, such because the unanticipated growth of psychiatric issues, might be studied nearer to residence.
NASA and different establishments are presently learning all this on the ISS and might want to proceed such analysis lengthy past the area station’s retirement—one purpose why it’s crucial that another person launch a successor area station, and shortly. To that finish, simply because it did with SpaceX from 2006 by 2011, the company has seeded a number of corporations with small investments, promising to lease area on emergent area stations. And proper now, the soonest more likely to launch is being led out of a sprawling former Fry’s Electronics retail retailer in a shopping mall complicated in Texas.
I met Michael Baine, the chief expertise officer of Axiom Area, on a grey, drizzly January morning on the entrance to its Area Station Growth Facility in Houston. Baine started his profession at NASA Johnson Area Heart simply down the highway, the place he labored on every part from the shuttle and station to experimental lunar landers. Later, he left the company to affix Intuitive Machines as its chief of engineering. In February, that firm’s Nova-C spacecraft, Odysseus, grew to become the primary US spacecraft to land efficiently on the moon because the finish of the Apollo program in 1972, making Intuitive Machines the primary non-public firm to land efficiently on a celestial object past Earth. Baine has labored at Axiom Area since 2016. The startup’s long-term purpose is to construct the primary non-public industrial area station. It has efficiently organized and managed three non-public missions to the Worldwide Area Station, largely to check firsthand how people work and dwell in area, in order that they may design a extra user-friendly product.
Axiom isn’t the one firm keen on launching non-public area stations. Most notably, Blue Origin introduced in 2021 that in partnership with the aerospace outfit Sierra Nevada, it might construct Orbital Reef, a “mixed-use enterprise park” able to supporting as much as 10 individuals concurrently in low Earth orbit. In January, Sierra Nevada efficiently stress-tested a one-third-scale take a look at article of its habitat module, with the intention of launching a station into orbit on a Blue Origin New Glenn rocket in 2027. Different corporations, equivalent to Lockheed Martin, have made strikes into the market, although their progress is much less clear.
Axiom plans to construct its personal orbital facility a lot otherwise, Baine instructed me as we entered the ability. Suspended from the wall above, giant, low-fidelity fashions of spacecraft hung from the ceiling, together with the X-38 (an experimental emergency return automobile for area station crew) and Zvezda, the Russian module of the ISS, which at present is affected by age-induced stress fractures and consequent leaks. Crew automobiles now not dock with it.

expertise officer of Axiom Area, started his profession at NASA Johnson Area Heart.
“It’s very tough to construct a full, self-sustaining area station and launch it in a single shot,” Baine mentioned as we walked previous an open-concept dice farm beneath the fashions, the place about 500 women and men are designing an area station to exchange Zvezda and the remainder of the ISS. “What you wish to do is assemble it in area in a piecemeal style. The best manner to try this is to start out with one thing that’s already there.”
That “one thing” is the Worldwide Area Station itself. In 2026, Baine expects to launch Axiom Hab One, a cylindrical module with crew quarters and manufacturing capabilities that can plug into an open port on the ISS. Later, Axiom plans to launch Hab Two, increasing habitation, scientific, and manufacturing companies. Then it hopes to launch a analysis and manufacturing facility, full with a spacious, totally glassed cupola to present Axiom astronauts and guests on the station entry to an entire view of planet Earth, in addition to the size of the station. Lastly, the corporate intends to launch a “energy thermal module” with large photo voltaic panels, expanded life assist capabilities, and payload capability.
“We wished to show over the keys to the shuttle, the station—all that—to the non-public sector.”
Lori Garver, former deputy administrator of NASA
Every new section is designed to plug into the previous Axiom section. This isn’t aspirational; there’s a onerous deadline in impact. Except the ISS will get a brand new lease on life, every part should be launched and assembled by 2030. As soon as NASA formally declares the ISS mission accomplished, the Lego-like Axiom Station will detach from the ISS as its personal built-in and totally self-sustaining area station. Afterward, the deorbit automobile will do its job and push the ISS into the ocean.
“It’s a giant danger discount for us to have the ability to use ISS as a staging level to construct up {our capability} one ingredient at a time,” Baine explains. That plan additionally presents an enormous industrial benefit. There’s already a strong, international consumer base of corporations and researchers sending tasks to the ISS. “As a way to court docket these customers emigrate to a industrial resolution, it simply turns into simpler in the event you’re already at a location the place they’re at,” he says. Every part from technical interfaces to the way in which Axiom Station will deal with the outgassing of supplies might be suitable with present ISS {hardware}: “Now we have to satisfy the identical requirements that NASA does.”
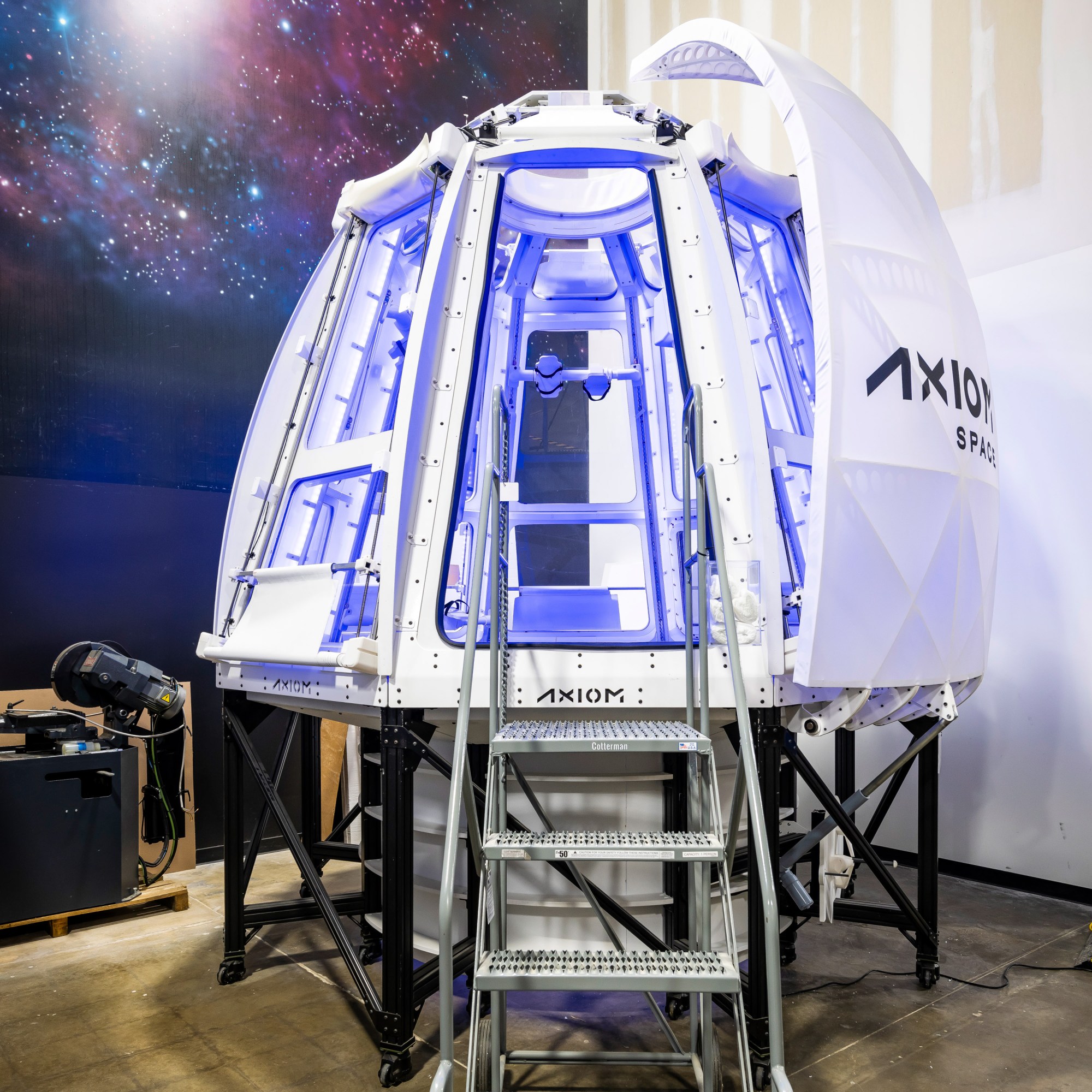

Lots of people are betting that there are fortunes to be made in LEO, and due to that, the US taxpayer isn’t paying for Axiom Station. Although NASA intends to ultimately hire area on Hab One, and has already awarded tens of hundreds of thousands of {dollars} to kick off early growth, the industrial station is being constructed by a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of personal {dollars}. The cultivation of business analysis and manufacturing is ongoing, which was NASA’s purpose going all the way in which again to Dan Goldin’s tenure as administrator.
“We wished to show over the keys to the shuttle, the station—all that—to the non-public sector,” says Lori Garver, a former deputy administrator of NASA and writer of Escaping Gravity. “Dan believed if we may hand over low-Earth-orbit infrastructure, NASA may go farther into area, and I actually purchased into that.” Garver would later pioneer the industrial spaceflight mannequin that led SpaceX and different corporations to take over launch companies, saving the company tens of billions of {dollars} whereas concurrently rushing launch cadence—the identical mannequin that led to Axiom’s area station work.
“After launching the primary module in 1998, we introduced that area was open for enterprise,” Garver instructed me. The primary particular person to achieve out was Fisk Johnson, of S.C. Johnson & Son. He wished to work with NASA to develop a bioreactor to assist create new prescribed drugs for liver illness in a microgravity atmosphere. “I labored with him for in all probability three years at NASA,” Garver says. “Sadly, their flight mission was Columbia, and we misplaced the experiment within the tragedy.”
Within the a long time to comply with, industrial analysis and growth would enhance, with limitations. NASA, Russia, and the opposite accomplice nations didn’t design the ISS particularly as a large-scale analysis and manufacturing facility, and one purpose no firm has elected to easily purchase the station outright is that refurbishing it might be extra complicated and costly than both constructing a brand new station, as Axiom has elected to do, or renting area on a contemporary successor.
As we stumbled on a shocking, full-scale mock-up of Hab One on the far finish of the constructing, I requested Baine if beginning with the technical options already developed by NASA—the way in which environmental programs work, for instance—makes Axiom Station simpler from an engineering perspective.
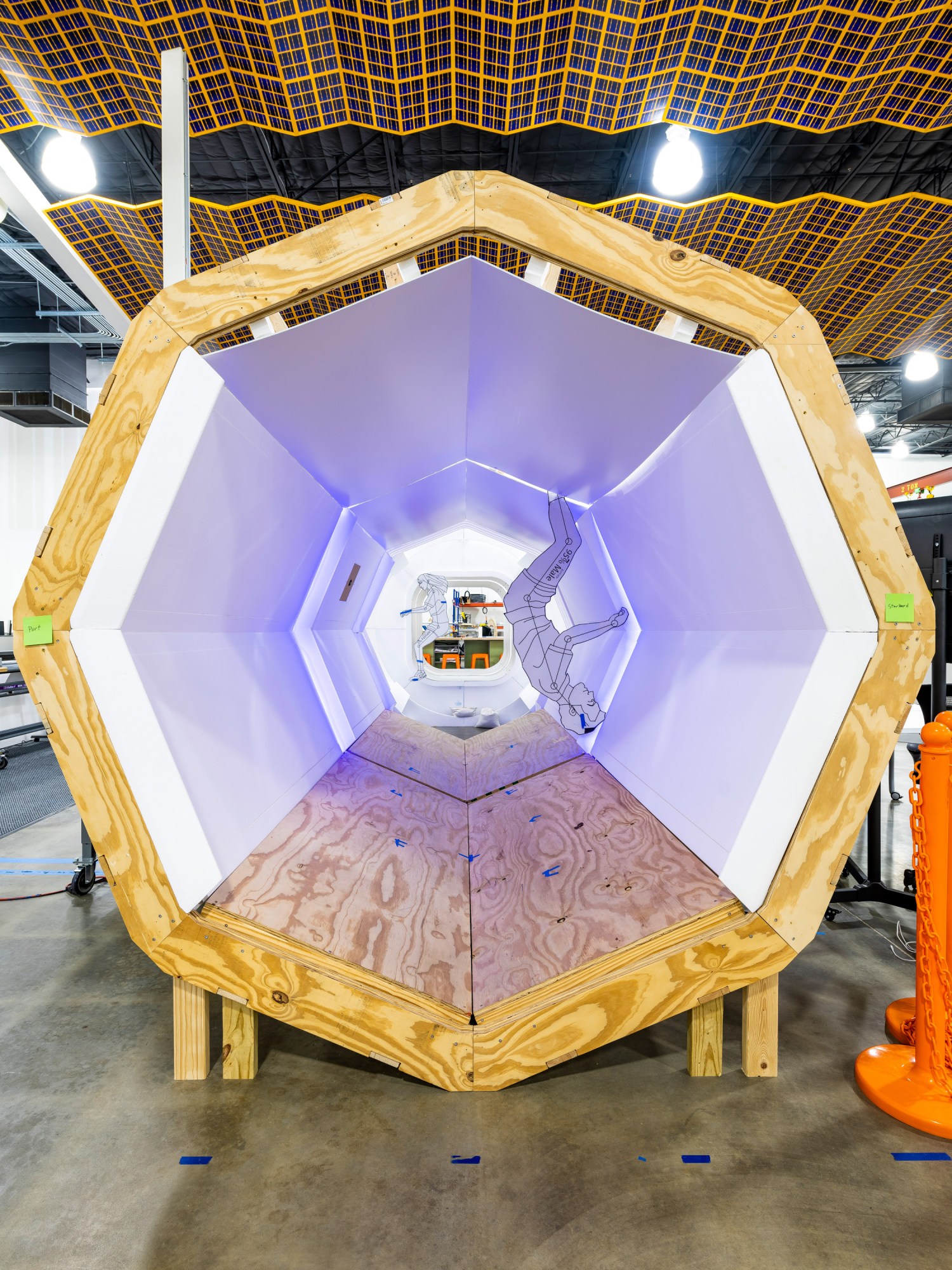

“You’d suppose so,” he replied, “however these are very demanding requirements, and so they require a whole lot of consideration to element.” The voluminous testing and analyses to show that you just meet the necessities essential to interface with ISS generate a whole lot of work, “however you find yourself with a construction or a element that’s extraordinarily dependable. The probabilities {that a} failure may propagate to a lack of crew could be very, very distant.”
Solely trying on the mock-up did I notice the immensity of the spacecraft. It’s 15 ft (4.6 meters) at its widest, and 36 ft lengthy. As soon as docked with the ISS, Hab One, which weighs 30 metric tons on Earth and might assist 4 astronauts, would be the longest ingredient on the station.
“It’s a spaceship-in-the-bottle downside. You principally should feed all of your programs by a 50-inch hatch.”
Michael Baine, chief expertise officer, Axiom Area
Right here on the Area Station Growth Facility, all the mock-up is product of CNC-machined wooden. However the module is far additional alongside than the existence of a “mock-up stage” would recommend. Its stress vessel (that’s, its major shell, which holds air and maintains an Earth-like stress atmosphere within the vacuum of area) and its hatches are basically accomplished and can quickly be shipped from Italy by the identical contractor that constructed many modules of the ISS. Baine walked me by a partitioned facility the place Axiom Station’s avionics, propulsion, life assist programs, communications, and different subsystems are effectively into growth. Befitting the previous Fry’s Electronics constructing during which we stood, there was a home-brew ingredient to the programs, lots of which had been strewn throughout tables—an elaborate net of wires, tubes, circuit boards, and chips. The station will run on Linux.
Axiom constructed the mock-up to unravel an nearly comically elementary problem that any venture equivalent to this faces: turning the stress shell and the myriad subsystems and parts right into a human-safe spacefaring automobile. You may’t simply drill holes within the stress shell, any greater than you’ll be able to punch a gap in a balloon and count on it to maintain its form. Axiom should construct the module inside and round it. “It’s a spaceship-in-the-bottle downside,” Baine mentioned. “You principally should feed all of your programs by a 50-inch hatch and combine them into the ingredient.” He calls it one of many hardest issues within the enterprise, as a result of it’s about greater than assembling programs inside a stress shell in Houston—it’s additionally about making the station consumer pleasant for servicing in orbit, if ever a technical situation arises.

is housed in a sprawling
former Fry’s Electronics
retail retailer in a purchasing
heart complicated.
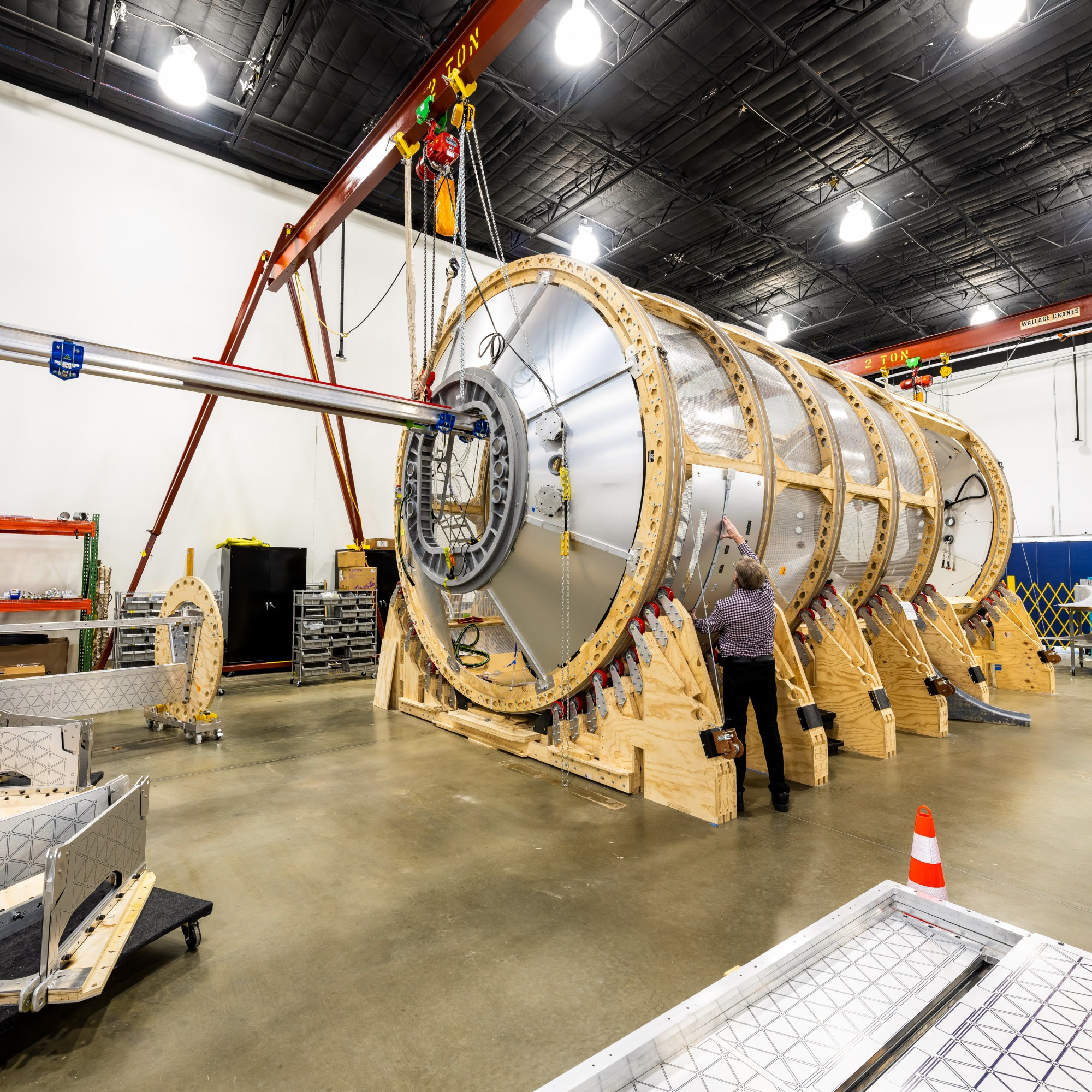

Habitat One (Hab One),
which can embody crew
quarters and manufacturing
capabilities.
In the present day, tourism and analysis are in all probability the best-known makes use of of personal spaceflight. However Axiom has different features in thoughts for the station, together with serving as a vacation spot for international locations which have but to get entangled in sending people to area. Final yr, the corporate introduced the Axiom Area Entry Program, which Tejpaul Bhatia, the corporate’s chief income officer, described as a “area program in a field” for international locations world wide. Axiom says this system is evolving, however that it’s a pathway for area participation. Azerbaijan was the primary nation to signal on.
However one of the vital promising enterprise prospects for the fast future is manufacturing. Low Earth orbit is an particularly good atmosphere for making issues in three areas: prescribed drugs, metallurgy, and optics. Microgravity eliminates plenty of bodily phenomena that may intrude with delicate steps in manufacturing processes, yielding extra constant materials properties and buildings. Axiom and Blue Origin are betting that fashionable area stations constructed across the insights gleaned from a long time of ISS experimentation (however freed of its 1980s and 1990s expertise) pays dividends.
As a part of its push to encourage corporations to develop their very own area stations, NASA has dedicated to leasing area on those who meet the company’s stringent human-spaceflight necessities. Simply as with a serious purchasing heart, an “anchor tenant” can supply monetary stability and appeal to extra tenants. To assist this alongside, a US nationwide laboratory based mostly in Melbourne, Florida, is particularly funding and supporting non-aerospace corporations that may profit from microgravity analysis.
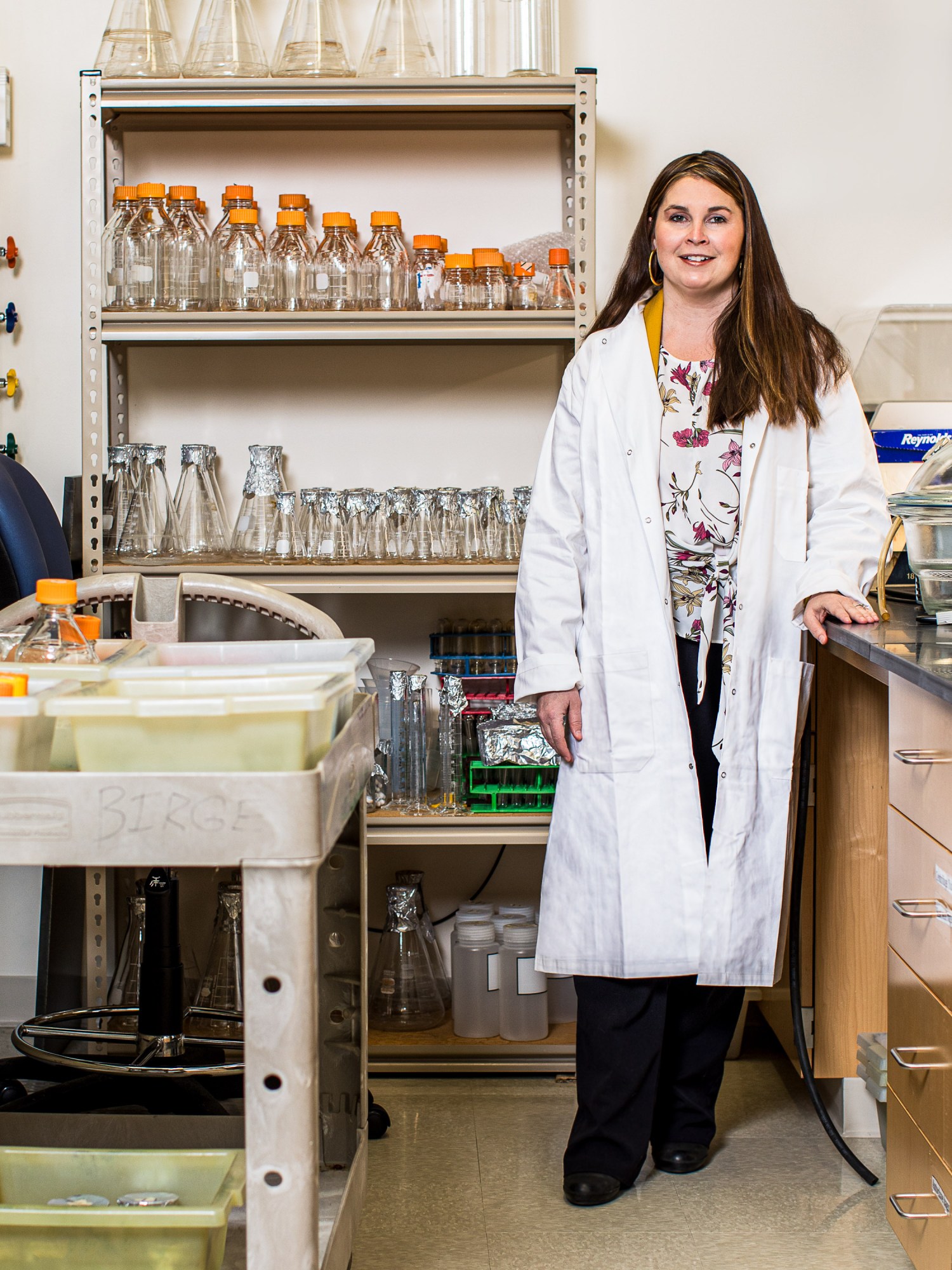
Biomedicine particularly has yielded maybe the very best outcomes with the nearest-term impression, as greatest represented by LambdaVision, an organization established in 2009 by molecular biologists Nicole Wagner and Robert Birge. What makes it probably the most compelling glimpse of LEO’s promise is that LambdaVision was not based as an aerospace firm. Relatively, Wagner and Birge had been constructing a standard, Earth-based firm atop their analysis on a protein known as
bacteriorhodopsin and its potential to revive neural operate. BR is a “proton pump,” which is simply what it appears like. It pumps a proton from one aspect of a cell to the opposite.
They targeted on the issues of retinitis pigmentosa and macular degeneration. In a wholesome eye, photoreceptor cells—rods and cones—absorb gentle and convert it right into a sign that goes to bipolar and ganglion cells, after which to the optic nerve. In each ailments, the rods and cones begin to die, and as soon as they’re gone, there’s nothing to soak up gentle and switch it right into a sign that may be despatched to the mind. Retinitis pigmentosa, which afflicts 1.5 million individuals world wide, begins by affecting peripheral imaginative and prescient and encroaches inward, resulting in extreme tunnel imaginative and prescient earlier than inflicting full blindness. Macular degeneration works the other manner, first affecting central imaginative and prescient after which spreading outward. About 30 million individuals world wide endure from it. Remedies exist for each ailments, however even the very best can solely gradual their development. In the long run, blindness wins, and as soon as it does, there isn’t any remedy.
Wagner, Birge, and their workforce at LambdaVision had an thought for one thing that may assist: a easy, versatile implant, about as massive because the circle stamped out by a gap punch and the thickness of a chunk of building paper, that would exchange the broken light-sensing cells and restore full imaginative and prescient. In precept, physicians may set up the patch at the back of the attention, the identical manner they deal with indifferent retinas, so it might not even require specialised coaching.
The issue was making this synthetic retina. The implant requires utilizing a scaffold—basically a tightly woven porous materials just like gauze—and binding a polymer to it. Atop that, the researchers start making use of alternating layers of BR protein and polymers. With sufficient layers, the protein can take in sufficient gentle and pump protons—hydrogen ions, particularly—towards the bipolar and ganglion cells, which take it from there, restoring imaginative and prescient in excessive definition.
To use a number of layers, scientists float the scaffold on an answer in a number of beakers, shifting from one to the subsequent and repeating the method. The issue is that fluid options are by no means good—issues float, they sink, they settle, they kind sediment, they evaporate, there’s convection, there are surface-tension variations—and each variation and imperfection can result in a flawed layer.

If an implant requires 200 layers, an imperfection at layer 50 compounds massively by the tip. The method is solely inefficient, and rife with irregular protein deposition. Early trials revealed that this situation negatively affected the synthetic retina’s efficiency.
It was the form of factor LambdaVision hoped to work by as a part of MassChallenge, a enterprise incubation program in Boston. Wagner was working within the enterprise accelerator’s co-working area in the future in 2017. It had a “Google-y” really feel, she felt, with an open-concept workplace and good individuals throughout, and she or he was on the desk they’d assigned her when any person dropped by to say that the Worldwide Area Station Nationwide Laboratory was holding a lunch presentation down the corridor, and there was free pizza.
Why not, Wagner thought. It might be fairly cool to listen to individuals from NASA speak concerning the moon and Mars. When she bought there, although, it turned out that it wasn’t that form of presentation in any respect. As a substitute, representatives from CASIS—the Heart for the Development of Science in Area, a nonprofit that operates the ISS Nationwide Lab—gave a chat on how they’re utilizing microgravity to assist individuals on Earth.
The US section of the Worldwide Area Station, like Los Alamos, Oak Ridge, and Brookhaven, is a nationwide laboratory devoted to scientific and technological analysis. The workplace merely has a greater view. About half the science performed on the US section is managed by the ISS Nationwide Laboratory out of Florida, with the rest overseen by NASA. This division of sources permits for a variety of scientific investigations on the station. The place NASA’s analysis sometimes focuses on exploration, area expertise, and elementary science to assist future deep-space missions, the ISS Nationwide Laboratory goals to develop a sustainable low-Earth-orbit financial system, encompassing fields like supplies science, biology, pharmaceutical analysis, and expertise growth.
“I by no means envisioned doing something in area—I didn’t know tips on how to get there, or the way it labored. Earlier than that second, all of it appeared like science fiction.”
Nicole Wagner, cofounder of LambdaVision
Analysis being performed on the station touches on metallurgy and fiber optics. Alloys like nitinol (nickel-titanium) can stand up to enormous temperature swings and are superelastic, with extraordinary potential for medical units, aerospace, and robotics. Suppose synthetic muscle tissue. The issue is that nitinol is extraordinarily onerous to make on Earth as a result of supplies settle out and warmth can get distributed erratically throughout manufacturing, which yields an unreliable product. The identical liabilities degrade the standard of fiber optics manufactured on Earth.
The answer to each is to go to area: in microgravity, warmth distributes extra uniformly and sedimentation doesn’t happen. Crystallization, the method of forming and rising crystals, is constant throughout lengthy distances with minimal degradation (which means pristine fiber-optic indicators whilst you develop throughout huge stretches). Extra broadly, nevertheless, space-based crystallography has purposes in nearly each discipline of electronics and biomedicine.
As Wagner discovered, researchers have discovered fast beneficial properties on the area station at present in every part from growth of simpler vaccines (gravity on Earth harms the interplay of antigens and adjuvants) to higher-grade drug formulations and nanoparticle suspensions. One such drug, made by Taiho Pharmaceutical, is used to deal with muscular dystrophy and has reached final-stage trials.
“They had been speaking at the moment about issues like bioprinting on orbit, and future missions they had been planning,” Wagner instructed me. “It hit me instantly that we may do that—really leverage microgravity to fabricate a synthetic retina. I by no means envisioned doing something in area—I didn’t know tips on how to get there, or the way it labored. Earlier than that second, all of it appeared like science fiction.”
After the assembly, she instantly known as her workforce. “There’s a prize that I believe we will win,” she mentioned. It was the CASIS-Boeing Know-how in Area Prize, which funds analysis that may profit from space-station entry. “We’re gonna do it.”
Her workforce was instantly skeptical. In reality, she had her doubts as effectively. She was operating a small startup. How had been they going to construct a small, automated science laboratory, put it on the Worldwide Area Station, have communication with it on the bottom—how would they afford that? She pulled up an online browser and typed in “raspberry pi communication with area station.” She thought: What am I stepping into?

“It was my super-naïve imaginative and prescient of what area was on the time,” she instructed me. The right time period that now described her firm, she quickly discovered, was “area adjoining”: a enterprise that’s not particularly within the aerospace business however may gain advantage from—even work higher by—leaving planet Earth.
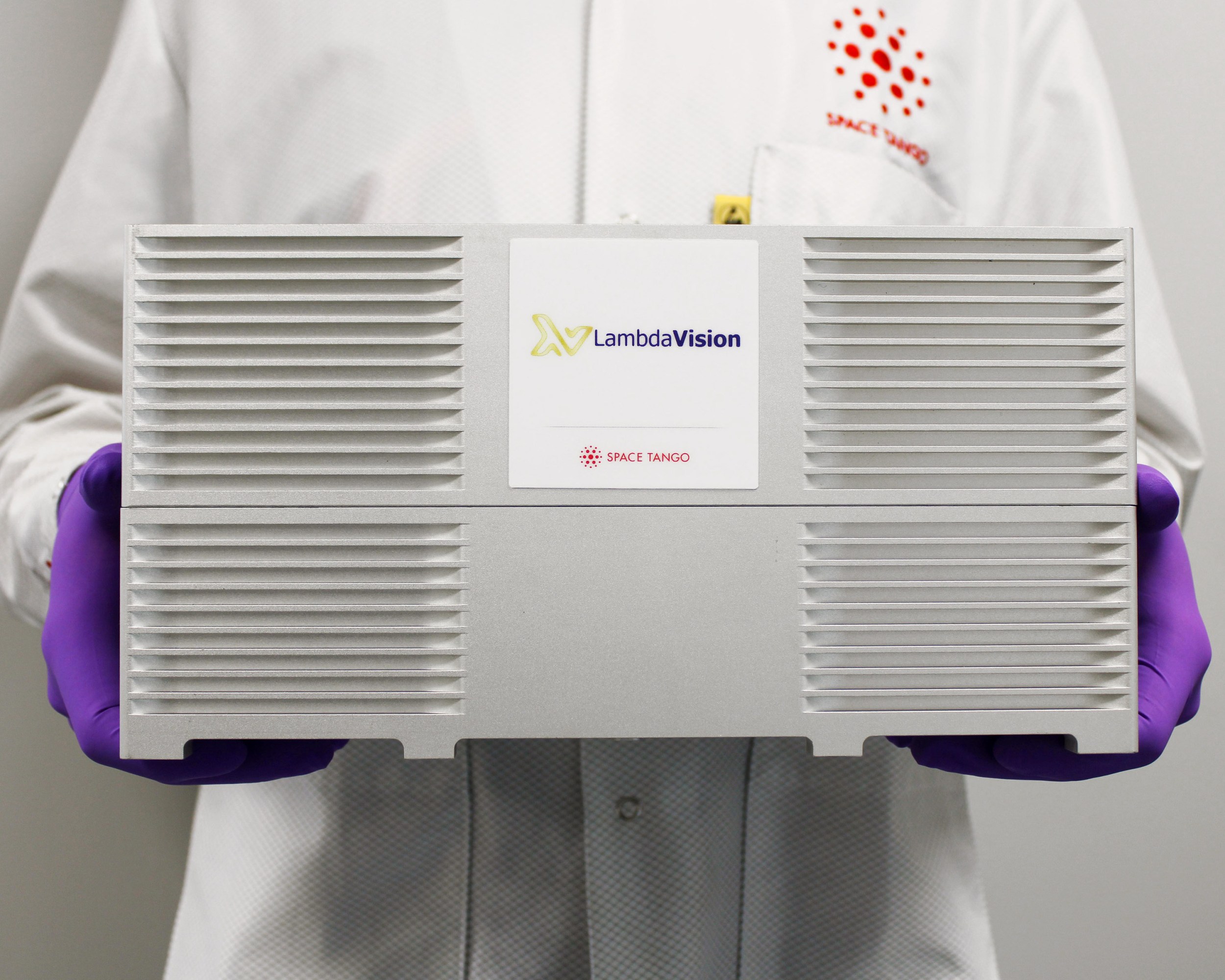
She was relieved when she discovered that LambdaVision didn’t should develop its personal mission management and area infrastructure. It already existed, and there have been accomplice corporations that specialised in space-adjacent companies. Her firm linked up with Area Tango, which focuses on constructing underlying well being and expertise merchandise in area, to develop its {hardware}. They managed to condense their open beaker system to an automatic experiment the scale of a shoebox. And she or he was proper about one factor: they did win the prize.
The workforce flew its first mission on the finish of 2018, and it confirmed promising outcomes. Within the years since, the corporate has secured further funding and flown a complete of 9 instances to the ISS, most lately launching on January 30. With every mission, they’ve step by step improved their manufacturing {hardware}, system automation and imaging, and orbital processes. “We’re seeing far more evenly coated movies in microgravity and overcome different challenges we see in a gravity atmosphere,” Wagner says. “There’s a lot much less waste.”
The system works autonomously, with out want of astronaut intervention. Primarily, the workforce assembles it in a small field, astronauts plug it into energy on the ISS, and when it has manufactured the sheets of synthetic retinas, an astronaut unplugs it and ships it again to Earth.
“At first, we simply wished to reveal that it’s possible to do that in area,” says Wagner. “We don’t fear about that now—we’re considering onerous now about scaling the system up. To assist our early medical trials, we don’t want hundreds of thousands of synthetic retinas. We’d like a whole bunch, perhaps hundreds, to start out. And that offers us time to find out how we’re going to scale that up as we transition from the ISS—a public area station—to non-public, industrial area stations in low Earth orbit.”
To this point, LambdaVision has carried out small-animal research in rats and superior to large-animal research in pigs, efficiently putting in the implants and demonstrating their tolerability. The corporate is constant preclinical growth to assist medical trials—doing things like testing the synthetic retinas for efficacy and security—with a purpose of starting human trials as quickly as early 2027.
“Once I take into consideration doing it in area and speaking about value and effectivity, I don’t give it some thought any otherwise than if any person mentioned, ‘Hey I’m gonna go do that in China’ or ‘I’m gonna go do that in California,’” Wagner says. “An area station is definitely nearer. It’s solely 250 miles within the sky, versus 3,000 miles to California.”
If LambdaVision is profitable, that alone would virtually justify the vote forged by John Lewis 31 years in the past. It’s onerous to consider an achievement extra profound than curing blindness for hundreds of thousands. However much more than delivering such sweeping and life-altering outcomes, one of the vital vital accomplishments of the ISS may be proving that such outcomes may even be achieved within the first place.
To this point, no main medicines born on the area station have been delivered to market. No mass-produced applied sciences have but emerged from low Earth orbit. Analysis has been iterative, and in-space manufacturing stays within the early levels. However in line with Ariel Ekblaw, CEO of the Aurelia Institute, a nonprofit area analysis heart devoted to engaged on “crucial path” infrastructure for area architectures, NASA’s groundwork for the ISS has made a subsequent technology of extra product-focused work potential.
“Possibly Dan Goldin was forward of his time in considering that such work was going to be achieved inside the time span of humanity’s first-ever really large-scale worldwide area station,” she instructed me, “and what we see now is not only primary science, however entities like biotech corporations really taking what we discovered from NASA and the Nationwide Lab over the past 20-plus years, and envision placing mass-produced merchandise or mass-produced infrastructure in area.”
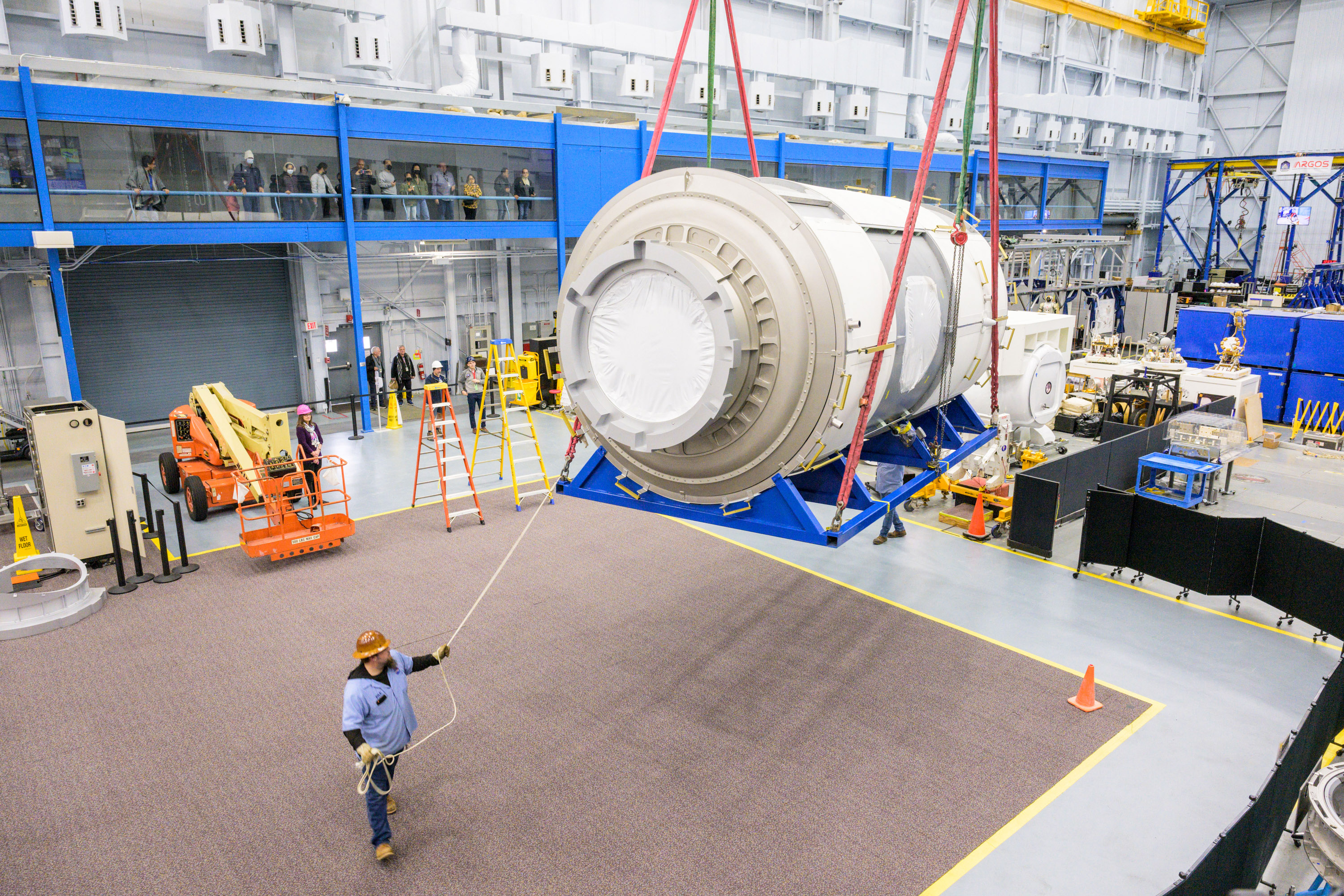

Habitation and Logistics
Outpost (HALO) module,
the primary element of
a deliberate moon-orbiting Gateway station.
If certainly the handoff of low Earth orbit from NASA-led to industrial operations succeeds, it might be a promising glimpse of the way forward for the lunar financial system. There, as in LEO, NASA is methodically constructing infrastructure and fixing elementary issues of exploration. The moon-orbiting Gateway station—a NASA-led worldwide effort—is deep into growth, with the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) module set to launch as early as subsequent yr. That station will function the “second step” of a sustainable moon technique that was excised from the Apollo program 60 years in the past. From there, NASA hopes to domesticate a presence on the lunar floor.
If the LEO mannequin holds, the company may in the future switch moon-base operations to the non-public sector and switch to Mars. There may be some huge cash to be made merely in harvesting water on the moon, to say nothing of uncommon earth components that lend themselves to manufacturing as effectively.
One of many harshest restraints on progress in area has been, satirically, area. “Proper now, on day, solely 11 individuals slot in orbit on ISS and Tiangong,” says Ekblaw. The age of personal area stations goes to be basically transformative if solely as a result of there might be extra room for devoted researchers.
Axiom’s purpose is to double its infrastructure in area each 5 years. This implies doubling the variety of individuals in orbit, the variety of hosted payloads, and the quantity of producing they’re able to doing.
“Inside two to 3 years, I may ship a graduate scholar to area with Axiom,” Ekblaw says. “It requires a bit artistic fundraising, however I believe that that’s opening up a realm of risk.” Prior to now, she explains, a doctoral researcher can be unbelievably lucky to have analysis fly as a part of a single flight mission.In the present day, nevertheless, researchers even in a grasp’s program can fly experiments repeatedly due to the elevated alternatives afforded by industrial spaceflight.Sooner or later, moderately than counting on profession NASA astronauts—who’ve myriad duties in orbit and spend period of time as guinea pigs themselves—scientists may go up personally to run their very own analysis tasks in higher depth.
“And that,” she says, “is a future that could be very, very close to.”
David W. Brown is a author based mostly in New Orleans. His subsequent e-book, The Outdoors Cats, is a few workforce of polar explorers and his expedition with them to Antarctica. Will probably be printed by Mariner Books.