The urgency of the worldwide transition to a net-zero financial system, targeted on options that allow the discount of greenhouse fuel emissions, can’t be overstated. As each the engine of worldwide financial progress and substantial emissions generator, trade has a singular accountability and alternative to guide this course of. And whereas the vitality and petrochemicals sectors have understandably been a central focus of those efforts, decarbonization is important throughout all industries.

Digital applied sciences might be key to the net-zero transition. They permit decarbonization with their potential to course of extra knowledge extra successfully, establish issues sooner, and check options nearly. Power-intensive programs will more and more discover effectivity positive aspects from digital and Web3 applied sciences similar to cloud and edge computing, synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML), web of issues (IoT) sensors, and blockchain expertise.
Knowledge is rising on the impression of digital applied sciences on greenhouse fuel (GHG) emissions, and their significance is obvious. The World Financial Discussion board (WEF) and Accenture say digital applied sciences may also help the vitality, supplies, and mobility industries scale back emissions by 4% to 10% by 2030.1 PwC calculates that AI alone can scale back international GHG emissions by 4% by 2030,2 whereas Capgemini experiences that the local weather potential of AI places the determine at 16% throughout a number of sectors.3
Regardless of these applied sciences’ confirmed impacts, nevertheless, organizations have inadequate urgency round their adoption to speed up decarbonization and emissions discount targets. Throughout trade, many leaders leverage companions to assist digital transformation, whereas vitality transition stays a secondary goal. Digital and sustainability leaders are taking a surprisingly conservative strategy to expertise that fails to handle present issues. As justification, they cite immaturity of current options, a necessity for additional research or customization, and challenges starting from intermittent renewable vitality provides to lack of belief in current carbon buying and selling schemes.
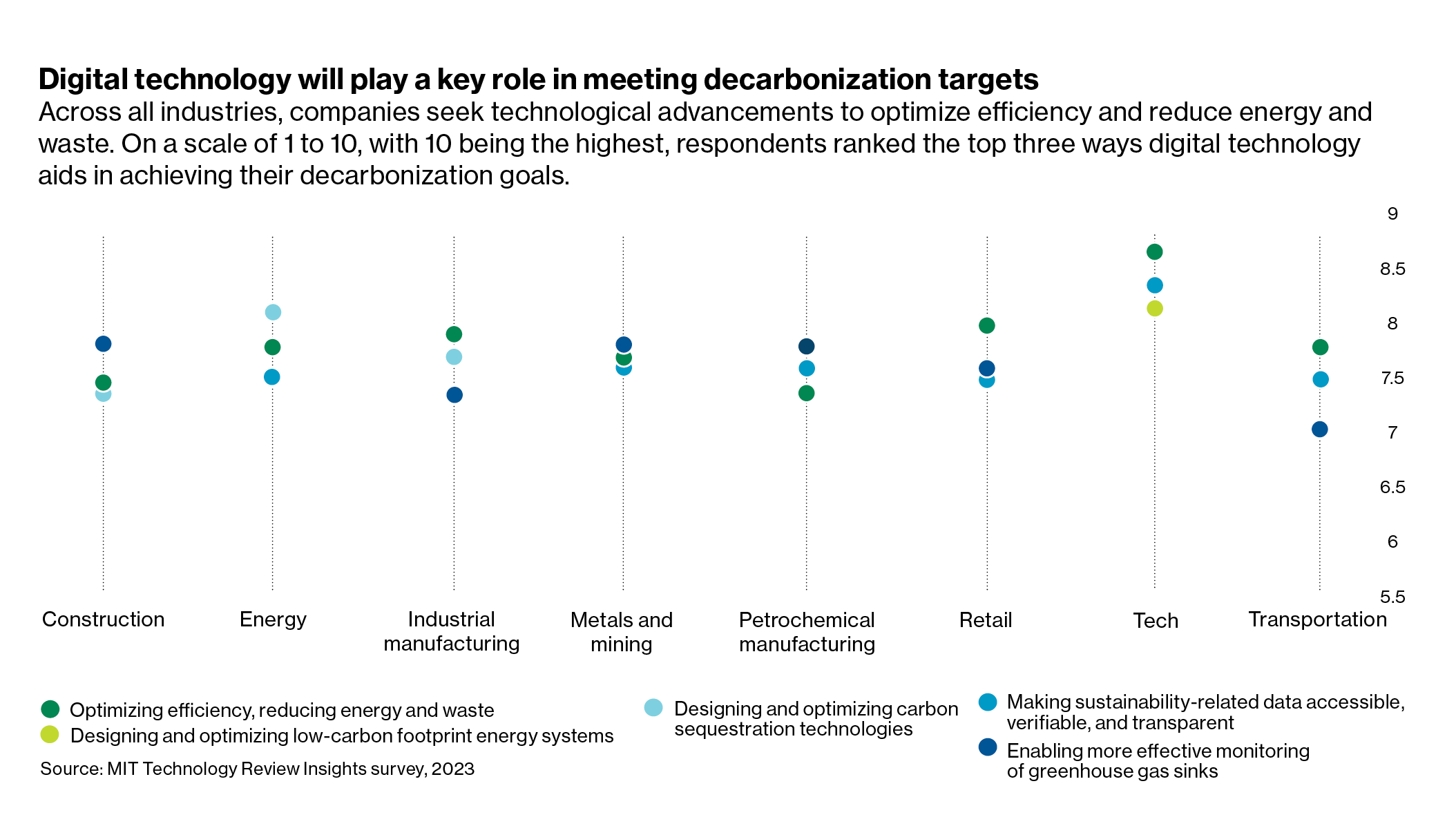
MIT Expertise Assessment Insights carried out a worldwide survey to look at trade leaders’ use of, plans for, and preparedness to undertake digital applied sciences to achieve decarbonization targets. The survey addressed 350 C-level leaders at giant international firms in eight main sectors, to assemble their perceptions about these options. Insights had been additionally gathered from in-depth discussions with 9 material specialists.
The next are the important thing analysis findings:
Digitalization is the spine that can assist vitality transition. Regardless of variations throughout industries (and throughout areas), digital applied sciences are thought of necessary (rated from 1 to 10, the place 10 is most necessary) for optimizing effectivity and decreasing vitality and waste (scoring 6.Eight general); designing and optimizing carbon sequestration applied sciences (6.7); making sustainability knowledge accessible, verifiable, and clear (6.2); monitoring GHG sinks (6.6); and designing and optimizing low carbon footprint vitality programs (5.8).
For many industries, the primary decarbonization lever is a round financial system. A majority (54%) of individuals from all industries (apart from petrochemical manufacturing) cite a round economy4 as their dominant environmental sustainability objective. A round financial system minimizes waste with diminished consumption, elevated effectivity, and useful resource and vitality recapture. The second most extremely rated sustainability objective is to enhance entry to scrub vitality (41%), and third, to enhance vitality effectivity (40%).
Partnership with expertise specialists is how trade innovates with digital options. Probably the most cited strategy to adopting new digital expertise is thru vendor partnerships (31%). Executives are much less doubtless, nevertheless, to emphasise the significance of open requirements and knowledge sharing throughout the provision chain to speed up digital expertise deployment (particularly in vitality, metals and mining, building, and petrochemical manufacturing), with solely 16% figuring out it as the highest enabler. But, specialists say an embrace of open requirements and knowledge sharing—important to AI and ML’s potential to overcome complexity—to streamline the provision chain is “inevitable” to assembly decarbonization targets.

Attitudes towards tech adoption and innovation fluctuate by sector and area. Though cybersecurity is taken into account the largest exterior impediment to digital transformation general (58%), building firms are far more apprehensive (76%), whereas metals and mining firms are much less involved (47%). General, 11% of respondents purpose to experiment with digital expertise early on, however some sectors are much less enthused: solely 4% in metals and mining, 5% in petrochemical manufacturing, and 6% in industrial manufacturing. Purchase-in and a willingness to be taught is important for cooperation throughout departments and organizations.
A digital tradition is required to know and tackle the challenges of decarbonization. The response to new expertise options is embedded in tradition, however the second commonest means firms attempt new applied sciences is by merely ready for them to mature (24%). Just one in 4 respondents wish to undertake a digital innovation tradition primarily based on data sharing and a studying mindset (25%). Expertise roadmaps (19%) and senior management (17%) have comparable, lesser affect. The success of adopting digital expertise relies upon not simply on the provision of knowledge, however on programs and personnel. It falls to management to construct digital coalitions of inner and exterior stakeholders, to encourage willingness to digitally rework, and clarify the significance of integrating digital applied sciences.
Obtain the report.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Expertise Assessment. It was not written by MIT Expertise Assessment’s editorial workers.